introgress
Version 1.22 of introgress was released in January 2010 and was available from CRAN, the main repository for R packages. It has now been archived and is no longer maintained or developed. If you are looking for a replacement, consider gghybrid or bgc.
See Changelog below.
introgress implements analyses that are described in Gompert and Buerkle (2009). The software and its use are described in Gompert and Buerkle (2010).
Please note that while introgress does a fine job at summarizing and detecting variation in introgression among loci, it does not necessarily lead to strong inferences about the causes of the variation (e.g., detection of selected loci). For example, variation can arise due to genetic drift and does so commonly under certain reasonable conditions. For detecting expectionally differentiated loci, with less sensititivity to genetic drift, we suggest using bgc. Please see Gompert and Buerkle 2012 for a comparison of bgc and introgress. In both cases please be aware of the mutliple evolutionary processes that can lead to expectional differentiation.
- Gompert, Z. and C. A. Buerkle. 2009. A powerful
regression-based method for admixture mapping of isolation
across the genome of hybrids. Molecular Ecology 18: 1207-1224
(article).
- Gompert, Z. and C. A. Buerkle. 2010. introgress: a software package for mapping components of isolation in hybrids. Molecular Ecology Resources 10: 378-384 (article).
Installation instructions
Installing the package is simple. introgress will function on all operating systems for which R is available (Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows).
- Start up R. If you do not yet have R installed, instructions and downloads are here. Select a CRAN mirror that is geographically close to you and then download the appropriate software for your operating system.
- From within R, install introgress using one of
the following methods (a or b).
- At the command-prompt, paste in the following
command:
install.packages("introgress", dependencies=T)
You may be prompted to select a CRAN mirror from which to download the package. This downloads and installs introgress, as well as a few packages upon which introgress depends. - From R's graphical menu (Mac OS or Windows):
- For the Mac OS, choose R
Package Installer from the Packages & Data
menu item.
For Windows, choose Install package(s)... from the Packages menu item (see image below).
- On Mac OS, in the new graphical box that opens (see
image below), press the Get List button. This
will download a list of all available R packages. In
the list, select introgress and select the
Install Dependencies check-box below, and then
press the Install Selected button. This will
download and install introgress as well as a few
packages on which introgress depends.
On Windows, simply select the introgress package from the menu.
With both operating systems, you might be asked to select a CRAN mirror for your downloads; select one that is geographically close to your location.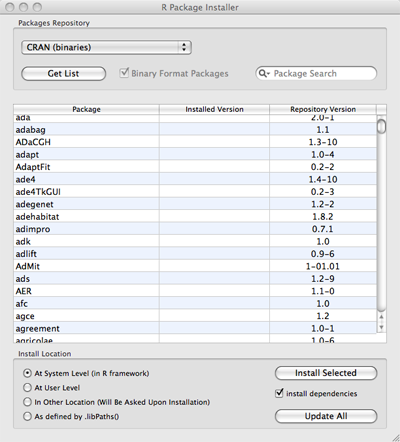
- For the Mac OS, choose R
Package Installer from the Packages & Data
menu item.
- At the command-prompt, paste in the following
command:
- Load the introgress package with:
library(introgress)
If this and the preceding steps worked, you should be ready to begin using introgress.
Please note that introgress utilizes the genetics package and the latter incorrectly warns that it is "obsolete". This warning can be ignored and will be removed in a future version of the genetics package.
Examples
-
The following text files contain data to be used in the example analysis from Table 2 in the manuscript (Gompert and Buerkle 2010) that describes the software (AdmixDataSim1.txt, LociDataSim1.txt).
-
The following is another example analysis and involves parental populations that share alleles. The code is in example.sim2.txt and should be used with the following data files: AdmixDataSim2.txt, LociDataSim2.txt, p1DataSim2.txt, p2DataSim2.txt.
Troubleshooting
-
Known problems:
- (Sept. 2009) With large numbers of alleles per locus (~45
alleles),
prepare.datamay run out of memory as it attempts to find combinations of alleles for the allelic classes. This will be fixed with a more efficient algorithm in a future version of introgress. Meantime, alleles that are known to be restricted to one of the parental taxa could be collapsed manually by the user, to reduce the number alleles thatprepare.dataencounters.
- (Sept. 2009) With large numbers of alleles per locus (~45
alleles),
-
CRAN mirrors may at times not be synchronized with the master CRAN in Austria. If you find that a certain package cannot be found on the mirror you have chosen, it is likely that you can find it by choosing another CRAN mirror that is nearby.
-
R Documentation -- R is a comprehensive environment for statistical computing and has many components. These components are documented in R's Help system, in online documents and manuals, and in many books. Have a look at the Documentation entry in the left sidebar on the R Project page.
Questions and feedback
We have tested introgress under a number of circumstances, with different data sets and operating systems, but surely there are situations that we have not anticipated. We welcome your feedback and will do what we can to assist you with the software.
If you have a question, a feature request, or encounter a bug, please consult the help pages for introgress, the manuscripts that describe the method and software and thoroughly investigate your concern or problem. If you are interested in a new feature, we encourage you to consider writing it and contributing it to the package. If our assistance is required, please send an email and provide as much information as possible. Over time we will likely build a FAQ.
- What operating system did you use (Windows, Mac OS, linux, etc., as well as version of operating system), what version of R and what version of introgress?
- Can you provide code and data that will allow us to reproduce your problem?
Changelog
- 1.22 (January 10) relative to 1.21 (October 09):
- Previously, large datasets could exhaust the available memory. We have modified the functions for significance testing to utilize less memory.
- 1.21 (October 09) relative to 1.2 (September 09):
- Fixed a bug in the parametric approach to signficance
testing. This bug has been in all previous versions of
introgress and affects the parental allele frequencies
that are used for simulations in the
genomic.clinesfunction. The bug was not present in R code we used for previous publications.
- Fixed a bug in the parametric approach to signficance
testing. This bug has been in all previous versions of
introgress and affects the parental allele frequencies
that are used for simulations in the
- 1.2 (September 09) relative to 1.1 (March 2009):
- The
compare.clinesfunction now allows for significance testing using a permutation procedure. - The
genomic.clinesfunction now allows for estimation of genotype specific deviations (i.e., quantile for the total probability of a genotype relative to the total probability of that genotype from permuted or simulated data sets). -
clines.plotallows for genotype specific deviations to be reported (+, - , or blank) above plots, with a user defined significance threshold. - The relevant documentation has been updated to reflect these changes.
- The documentation for
prepare.datanow explains how missing data should be entered.
- The
Grant support for work
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 0701757 (Plant Genome Research Program). Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recomendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation (NSF).
